Arctic Shipping Route: More Than Just a 25% Shorter Journey
China and Russia Collaborate to Develop Arctic Shipping Route
China and Russia will establish a subcommittee focused on the Arctic shipping route to promote its development as a vital international transportation corridor. The first meeting of the Arctic Route Cooperation Subcommittee took place on November 25th in St. Petersburg, Russia.
The Importance of the Arctic Shipping Route
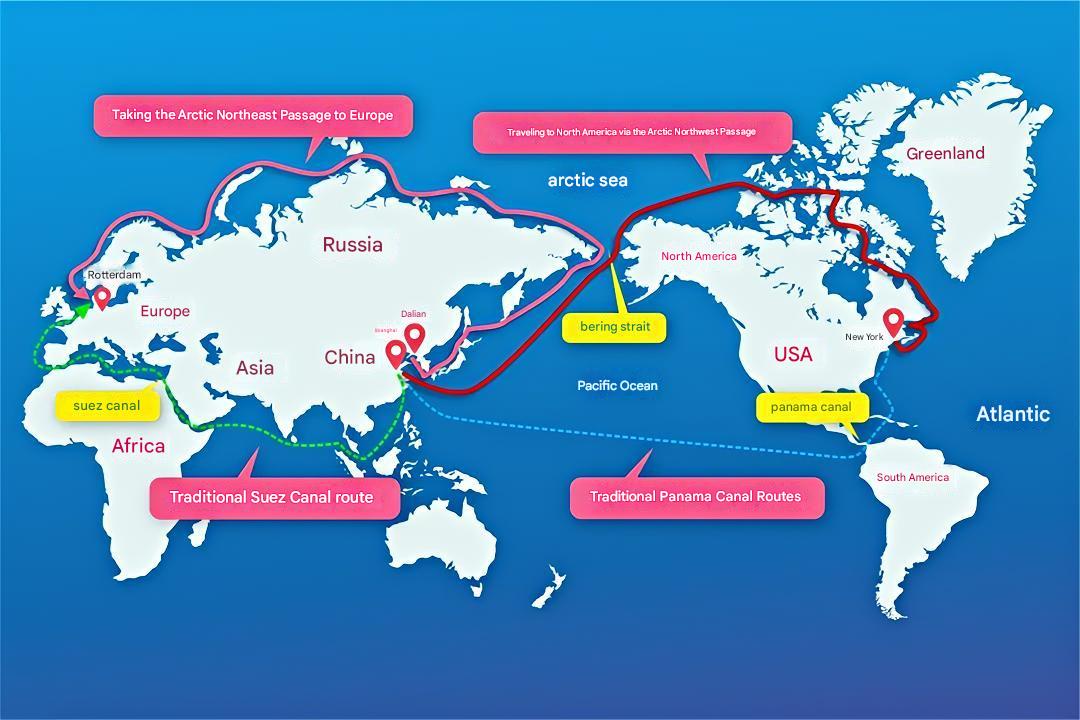
Traditionally, maritime logistics between China and Europe have relied on the Suez Canal, but this route is often affected by geopolitical events. The traditional shipping route from Shanghai, China, to Rotterdam, Netherlands, is about 20,000 kilometers. By taking the Arctic route, the journey can be shortened by 25%, reducing travel time by 10 to 15 days. Additionally, it allows vessels to avoid high-risk areas like the Strait of Malacca, the Indian Ocean, the Gulf of Aden, and Somalia, making the Arctic route a strategically important option.
From the image above, the Arctic route appears to be longer. However, this illusion is caused by the Mercator projection , which stretches areas horizontally as they get closer to the poles and compresses areas near the equator. When viewed on a globe, it becomes clear that the Arctic route is actually shorter than traditional routes.
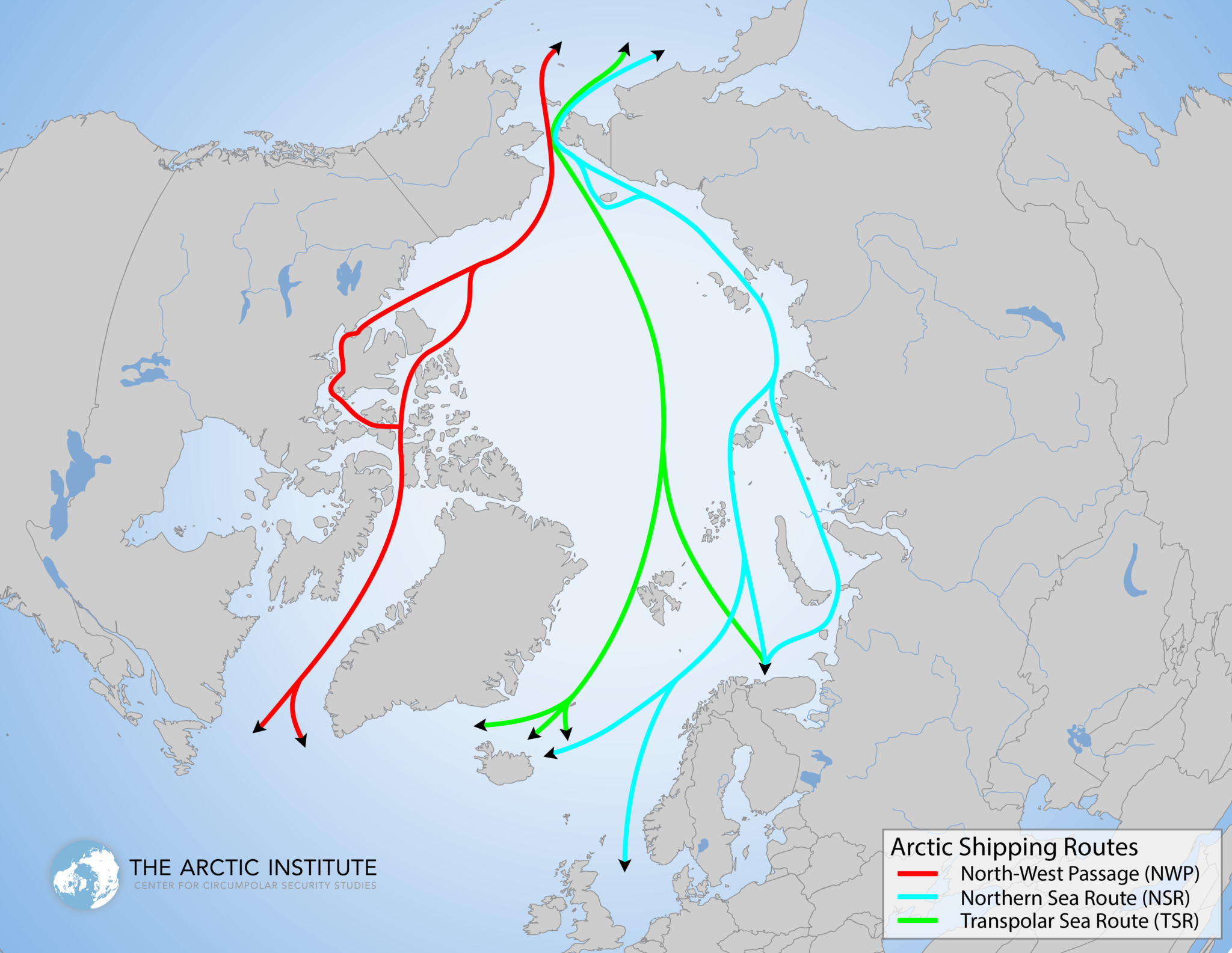
Strategic Implications for Global Trade
The Arctic shipping route offers a significant alternative to traditional shipping lanes. By reducing the travel distance and avoiding unstable regions, it has the potential to transform trade between China and Europe. The development of this route is not only about shortening journey times but also enhancing the security and reliability of maritime trade, which is increasingly crucial in the face of global trade uncertainties.

