Shipping Requirements for Lithium Battery Dangerous Goods

According to the classification of the *International Maritime Dangerous Goods Code* (IMDG Code), lithium battery goods belong to Class 9 dangerous goods. Depending on the specific product type, they are divided into seven entries, corresponding to the following UN numbers:
| UN Number | Class | Proper Shipping Name |
|---|---|---|
| 3480 | Class 9 | Lithium-ion batteries (including lithium-ion polymer batteries) |
| 3481 | Class 9 | Lithium-ion batteries packed with or contained in equipment |
| 3090 | Class 9 | Lithium metal batteries (including lithium alloy batteries) |
| 3091 | Class 9 | Lithium metal batteries packed with or contained in equipment |
| 3171 | Class 9 | Battery-powered vehicles or equipment |
| 3166 | Class 9 | Vehicles powered by flammable liquid/gas or hybrid systems |
| 3536 | Class 9 | Lithium batteries installed in cargo transport units |
When classifying lithium battery dangerous goods, attention must also be given to the "Special Provisions" associated with each UN number. These provisions detail exemptions, packaging, and transport requirements.
2. General Requirements for Lithium Battery Dangerous Goods
- Batteries must comply with the testing requirements of Section 38.3 of the UN Manual of Tests and Criteria.
- Each cell and battery must have a safety vent and be designed to prevent rupture under normal transport conditions.
- Effective devices must be in place to prevent external short circuits.
- Batteries containing multiple parallel cells must have protection against reverse current (e.g., diodes, fuses).
- Manufacturing must adhere to high-quality management systems, including design, quality control, inspections, and training programs.
- For electric and hybrid vehicles, measures should be taken to prevent unintentional activation during transit.
3. Container Packing Requirements
- Containers must be in good condition and certified by a classification society.
- Ensure the interior of the container is clean, dry, and free of damage or contamination.
- Packing must meet the requirements of GB 40163, including proper stacking, securing, and padding.
- Goods should be evenly distributed, with no more than 60% of the total weight concentrated within half the container length.
- If protective covers are used, labels and markings must remain visible on the cover surface.
- For Full Container Load (FCL) shipping, ensure that the entire container is used exclusively for your shipment, minimizing the risk of cross-contamination with other goods.
- FCL shipping allows for greater control over the loading and securing process, ensuring compliance with the strict safety and regulatory requirements for lithium battery transport.
- By using a dedicated container, you ensure that all hazardous materials, including lithium batteries, are securely packed and isolated from other cargo.
4. Labeling, Marking, and Placarding Requirements
Container Marking
- Except for vehicles driven by lithium batteries (pure electric or hybrid), containers containing lithium battery hazardous goods must have Class 9 hazardous goods labels and UN number markings affixed to each side and each end of the container (for lithium-ion battery energy storage systems, on two opposite sides).
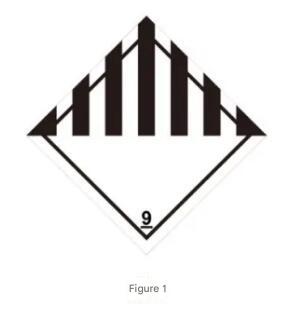
- The Class 9 hazardous goods label is shown in Figure 1. The minimum size of the label is 250mm*250mm, with the inner border line parallel to and 12.5mm away from the edge. The label should be affixed in a position with a contrasting background color against the container itself or have a visible border line.
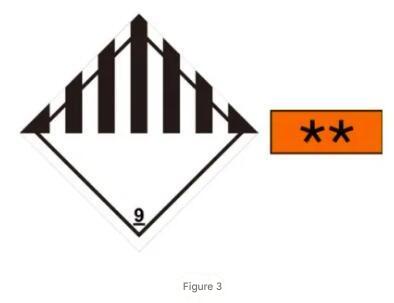
- The UN number should be displayed in black digits with a height of no less than 65mm. It can be affixed in the area between the symbol and the category number on the hazardous goods label, as shown in Figure 2. Alternatively, it can be affixed to an orange rectangular plate with a minimum height of 120mm, a width of no less than 300mm, and a 10mm black border around the edge, as shown in Figure 3, positioned close to the hazardous goods label.

Package Marking
- Except for containerized lithium-ion battery energy storage systems and vehicles powered by lithium batteries (pure electric or hybrid), each package containing lithium batteries must be labeled with the correct shipping name and the corresponding UN number prefixed with the letters "UN." The height of the UN number and the letters "UN" must be at least 12mm.
- Except for containerized lithium-ion battery energy storage systems and vehicles powered by lithium batteries (pure electric or hybrid), packages containing lithium batteries or battery packs must be affixed with the 9A dangerous goods label as shown in Figure 4 or the lithium battery mark as shown in Figure 5, as required.


5. Port Declaration Requirements
Declarant
The owner or their agent is responsible for the declaration.
Required Documents
- Declaration of Dangerous Goods Compliance
- Container packing certificate signed by an inspector
- Packaging compliance certificate, if applicable
- Proof of authorization, along with identification of the consignor and consignee
- In addition to the above, it is essential to ensure proper Customs Clearance procedures are followed. This includes submitting accurate declarations and ensuring that all documentation aligns with international regulations for dangerous goods.
- Failure to comply can result in delays and fines, making customs clearance a critical part of the shipping process.
To ensure a smooth and cost-effective shipping process for lithium batteries, businesses must consider several crucial aspects beyond the basics. These include freight cost estimation, effective warehousing strategies, selecting the right freight solution, and leveraging digital logistics tools. Each of these factors plays a vital role in streamlining operations, ensuring compliance with regulations, and optimizing costs throughout the shipping process.
Freight Cost Estimation for Lithium Battery Shipments
- Estimating the cost of shipping lithium batteries is crucial for effective budget management.
- Factors like weight, volume, and shipping method (whether air freight, sea freight, or road freight) influence the final cost.
- Utilizing freight calculators can help businesses determine accurate shipping estimates.businesses determine accurate shipping estimates.
- Packaging and safety requirements should be factored into the overall cost.
- Account for additional fees for hazardous goods to avoid unexpected expenses during transit.
Warehousing and Logistics for Lithium Battery Storage
- Proper warehousing of lithium batteries is essential to maintain their integrity and comply with safety regulations.
- Warehouses should be equipped to handle hazardous materials, ensuring lithium batteries are stored in dry, cool environments, away from heat or direct sunlight.
- Efficient logistics management ensures inventory is handled properly and prepared for timely shipping.
- A clear warehousing strategy streamlines the shipping process and ensures your goods are ready for transit without delays.
Digital Logistics Tools for Managing Shipments
- Digital logistics tools streamline the management of lithium battery shipments.
- Use real-time shipment tracking for efficient monitoring.
- Inventory management is simplified through digital solutions.
- Freight forwarders and businesses can use tools to track deliveries and optimize routes.
- These tools increase efficiency and reduce errors, ensuring safe handling of hazardous materials.
For expert solutions in shipping lithium batteries, including cost estimation, warehousing, and logistics, we're here to help. Contact us today for personalized support and seamless transportation of your hazardous goods.

