Under CIF and Shipped by LCL: Who Pays Destination Port Charges?
What is CIF?
CIF stands for Cost, Insurance, and Freight, where the seller is responsible for paying the freight charges to deliver goods to the buyer's port of destination, as well as purchasing insurance. However, did you know that some CIF sellers ship goods to the destination port without fully paying the ocean freight? In some cases, they even make a profit from shipping!
Sea freight is a preferred mode of transport for international shipments due to its cost-effectiveness and capacity to handle large volumes. However, understanding the associated charges, such as destination port fees, is essential for effective budget planning in sea freight.
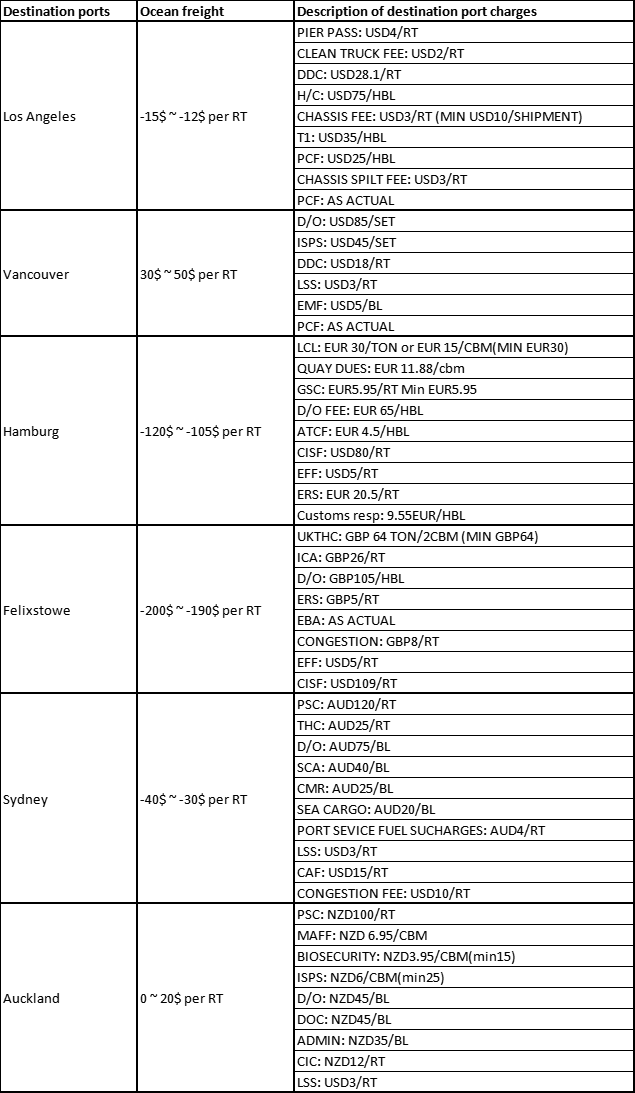
Understanding Ocean Freight and Destination Charges
Below is an example of how CIF terms and LCL (Less than Container Load) shipments interact with destination charges:
You might be wondering
- Why is the ocean freight sometimes a negative number?
- If the sea freight cost is negative, why haven't you received a refund from your CIF supplier or forwarder?
- Why is the ocean freight not negative in your CIF quotations?
Because
- The shipping cost and profit can be gained from the destination port charges.The division of ocean freight and destination port charges is determined between the freight forwarders at the origin port and the freight forwarders at the destination port.
- You were not aware of this because your CIF supplier may have profited from it, and they didn't want you know.
- The sea freight in the quotation provided by your freight forwarder is not negative number because both the ocean freight and destination port charges are collected by them. If the sea freight in the quotation is negative, it might cause confusion and misunderstanding, and processing a refund could also incur additional bank charges.
Example: LCL Shipment from Shanghai to Los Angeles
For a shipment of 10 CBM and 3 tons from Shanghai to Los Angeles:
- Shanghai forwarder pays/refunds the CIF factory approximately $150.
- Los Angeles forwarder charges the consignee $500 for destination charges.
Example: LCL Shipment from Shanghai to Hamburg
For a shipment of 10 CBM and 3 tons from Shanghai to Hamburg:
- Shanghai forwarder pays/refunds the CIF factory approximately $1100.
- Hamburg forwarder charges the consignee EUR 1500 for destination charges.
So, in some cases. Under CIF by LCL is not fair especially CIF factory dosen't advise how much the destination charges and get consignee/buyer's approval before shipping, consignee/buyer is pay more than factory/seller
In conclusion, Although destination charges are collected by destination port forwarder when shipment arrival, but the charges cannot be put to the consignee's responsibility based on where and when the occurrence under CIF terms. In my opinion, if the CIF supplier/shipper/seller does not prepay the destination charges, they should advise the consignee/buyer of the specific destination charges and get their approval. If shipment's quantity reach to a 20' container load and the CIF supplier insist on ship as LCL, you should be aware of that.
Lessons Learned from LCL Shipment in Hamburg
In January 2022, one of my German clients entrusted me with the customs clearance and delivery for two LCL shipments at Hamburg. Upon receiving the Arrival Notices from the destination port forwarder, I realized why the CIF supplier split the 30 cbm goods as two LCL shipments (one with 15.5 cbm and the other with 14.5 cbm) loaded into different containers on the same vessel from Ningbo to Hamburg. As a result, my client had to pay 3125.32 EUR for destination charges (as shown in the bills from the Hamburg forwarder below). If the shipments were shipped as one 20GP container, the destination charges could have been just 350 EUR. My client attempted to claim compensation from the CIF supplier, but the supplier rejected the claim, arguing that the shipments were already shipped to the destination port, and their responsibilities were fulfilled according to the CIF term.
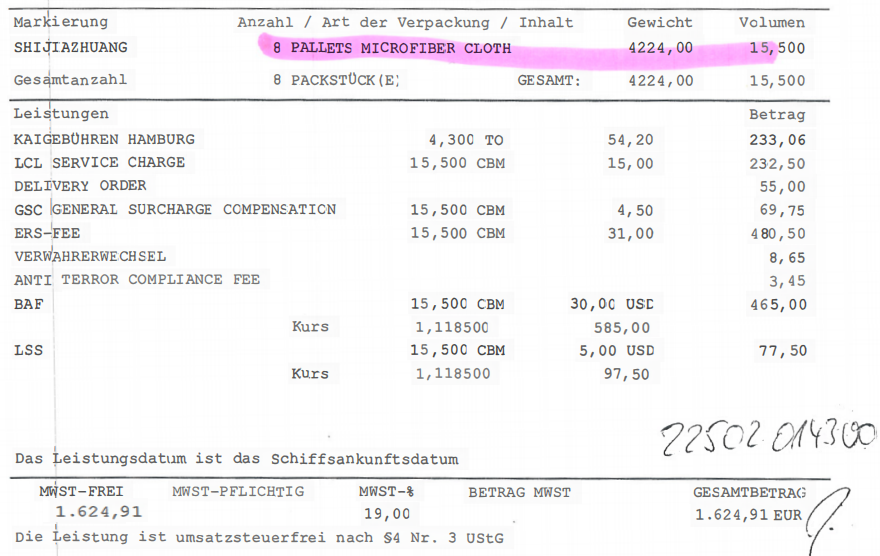
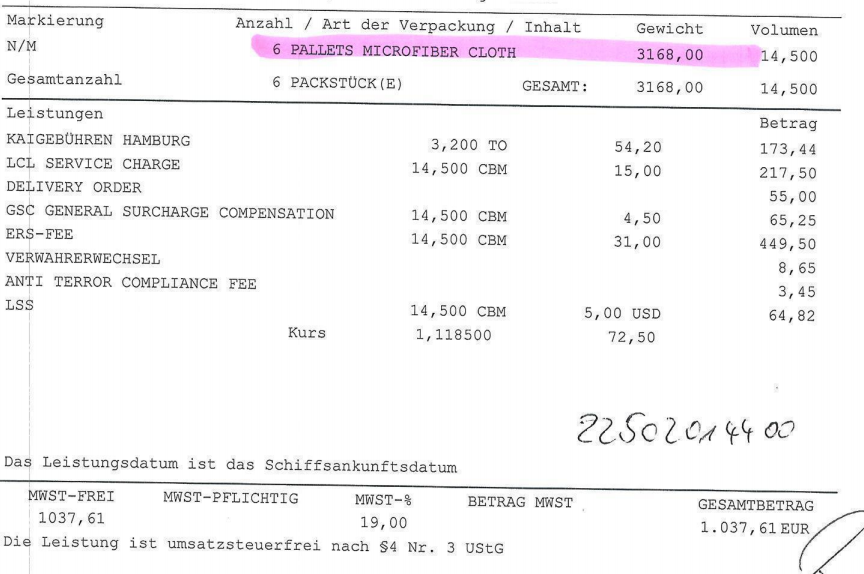
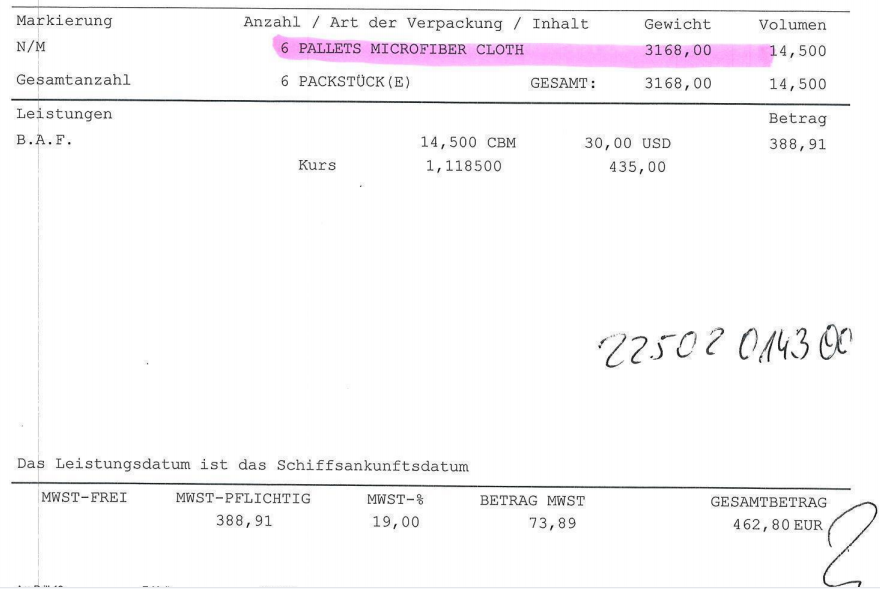
Be vigilant when suppliers insist on shipping LCL instead of a full container load (FCL) for larger shipments.
Conclusion
Under CIF terms, destination charges are collected by the destination forwarder upon arrival. However, these charges should not automatically fall on the consignee. Suppliers should communicate and obtain approval for these costs from the consignee in advance.
Stay cautious and protect your interests by clarifying terms upfront.
Suppliers should advise on destination port charges, especially when insisting on shipping LCL for larger quantities that could fit in a full container load (FCL). By understanding key aspects like warehousing, customs clearance, and specific shipping methods, you can avoid unnecessary costs and ensure smoother shipping processes.
In addition
-
FCL and LCL Shipping
In FCL (Full Container Load) shipping, the consignee typically pays the destination port charges. However, in LCL (Less than Container Load) shipping, these charges may be divided among multiple consignees based on their cargo volume or weight.
-
Ocean Freight
Ocean freight encompasses various charges, including loading, unloading, and destination port fees, which can vary depending on the shipping route and cargo type. These charges often reflect the complexity of handling diverse cargo types and the operational costs at different seaports. Proper knowledge of these charges ensures accurate cost estimation for businesses.
-
Freight Cost Calculator
-
Using a freight cost calculator can help businesses estimate the total expenses, including destination port charges, and avoid unexpected costs. By providing insights into various cost components, it enables better financial planning and ensures more transparency in shipping operations.
-
Shipping Container Loading Calculator
A shipping container loading calculator can optimize space utilization, reducing overall shipping costs and potentially lowering destination port charges. It also helps identify the most efficient container configuration, minimizing wasted space and ensuring cargo safety during transit.
-
Customs Clearance Service
Customs clearance services are vital for smooth cargo handling. These services, though an added cost, ensure that your goods comply with local regulations and reach their destination efficiently. They also help avoid potential delays and penalties, streamlining the shipping process and enhancing overall supply chain reliability.
-
Warehousing and Logistics
Destination port charges can also include warehousing and logistics fees if cargo requires temporary storage or further transportation beyond the port. Efficient warehousing solutions can reduce demurrage costs and help maintain the integrity of goods during transit.
-
Roll On Roll Off Shipping (RoRo)
Roll On Roll Off (RoRo) shipping is commonly used for vehicles. The destination port charges for RoRo shipments may include specialized handling fees due to the nature of the cargo. These fees often account for the secure loading, unloading, and movement of rolling cargo at the port.
-
Flat Rack Containers and Open Top Containers
Cargo transported in flat rack containers and open top containers may incur additional handling charges at the destination port, as these container types require specialized equipment for loading and unloading. Such cargo often includes oversized or irregularly shaped items, necessitating custom handling procedures.
-
Amazon FBA Warehouse Locations
For businesses using Amazon FBA services, understanding destination port charges is crucial, especially when shipping to regions near Amazon FBA warehouse locations, where logistics play a significant role. Optimizing shipping routes and synchronizing with warehouse schedules can further streamline operations and reduce costs.
FAQs
Who pays destination port charges in FCL and LCL shipping?
In FCL shipping the consignee typically pays destination port charges, while in LCL shipping, the cost may be shared among consignees.
How can a freight cost calculator help in shipping?
A freight cost calculator helps estimate the total shipping expenses, including destination port charges, enabling better budget management.
What are the additional charges for specialized container types?
Flat rack and open top containers often incur extra handling fees at the destination port due to their unique loading and unloading requirements.
What are the destination port charges in RoRo shipping?
In RoRo shipping, port charges include costs for vehicle handling and specialized equipment for loading and unloading.
How does container loading optimization reduce costs?
Using a shipping container loading calculator can maximize space utilization, lowering overall shipping costs and associated port charges.

